Understanding Pharmaceutical Folding: Precision in Medication Packaging
What is Pharmaceutical Folding? Pharmaceutical folding is a highly specialized process used in the production of folded informational inserts, leaflets, and labels for medical and pharmaceutical products. These materials provide essential details such as dosage instructions, safety warnings, and regulatory information. Given the strict industry regulations and the necessity for precision, pharmaceutical folding requires advanced…
Table of Contents
What is Pharmaceutical Folding?
Pharmaceutical folding is a highly specialized process used in the production of folded informational inserts, leaflets, and labels for medical and pharmaceutical products. These materials provide essential details such as dosage instructions, safety warnings, and regulatory information. Given the strict industry regulations and the necessity for precision, pharmaceutical folding requires advanced techniques, specialized machinery, and quality control measures to ensure accuracy and readability.
The Importance of Pharmaceutical Folding in the Healthcare Industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, every medication must include detailed information regarding its use, potential side effects, storage instructions, and contraindications. Due to limited packaging space, particularly in small medicine boxes, the inserts must be folded into compact, easy-to-store formats without compromising legibility.
Pharmaceutical folding plays a crucial role in:
- Ensuring regulatory compliance with FDA, EMA, and other health authorities.
- Providing clear and accessible patient information.
- Maintaining high production efficiency in large-scale pharmaceutical manufacturing.
- Reducing packaging waste and optimizing storage.
Pharmaceutical inserts are not only essential for patient safety but also serve as legal documentation, making their accuracy and precision critical.
Types of Pharmaceutical Folding
1. Parallel Fold
This type of fold consists of multiple parallel creases that allow the leaflet to be unfolded in a straightforward, systematic way. It is commonly used for instructions that need to be read in sequence.
2. Accordion Fold
An accordion fold consists of alternating folds that resemble a zigzag pattern. This type of folding is beneficial when dealing with large amounts of information that need to be neatly organized and easy to unfold.
3. Roll Fold
In a roll fold, the paper is folded inward multiple times, creating a roll-like structure. It is often used for compact packaging where inserts need to be small yet easily readable.
4. Cross Fold
Cross folding involves folding a sheet both horizontally and vertically to create a compact final form. This is commonly used for large instruction sheets that need to fit inside small packaging.
5. Map Fold
The map fold is similar to a cross fold but allows for a more structured unfolding process, making it easy for users to navigate complex information.
Each of these folds is designed to serve a specific purpose, depending on the size and structure of the insert, as well as the requirements set by pharmaceutical companies and regulatory bodies.
Challenges in Pharmaceutical Folding
The pharmaceutical folding process is a highly specialized task that requires a balance between precision, regulatory adherence, high-speed production, material selection, and stringent quality control. Because pharmaceutical leaflets contain critical medical information, any error in folding, readability, or compliance can have significant consequences. Let’s explore these challenges in more depth.
1. Precision and Readability
One of the most significant challenges in pharmaceutical folding is maintaining the readability of the printed content, even after multiple folds. Since pharmaceutical leaflets are often large sheets folded into compact sizes, ensuring that the text remains clear is a primary concern. Several factors contribute to readability issues:
- Small Font Sizes: To fit extensive information within limited space, pharmaceutical inserts often use very small font sizes. This increases the risk of text blurring, ink smudging, or letters becoming unreadable due to excessive creasing.
- Ink and Paper Compatibility: Some ink types do not adhere well to certain paper materials, causing smudging or fading. Additionally, improper drying times can lead to ink transfer between folds.
- Alignment and Margins: If the text is not perfectly aligned before folding, sections may be cut off or overlapped, making key information difficult to find.
To counter these issues, pharmaceutical companies invest in high-resolution printing technology and precise folding machinery that ensures consistency. Quality checks such as automated optical inspections help detect readability concerns before inserts are packaged.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Pharmaceutical inserts must adhere to strict global regulatory standards, which differ across countries. Regulatory agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) in the UK set guidelines for pharmaceutical inserts to ensure that patients receive accurate, clear, and legally compliant information. Some key compliance challenges include:
- Content Mandates: Inserts must contain dosage instructions, side effects, contraindications, and legal disclaimers in a specific format dictated by regulatory authorities.
- Translation Requirements: In regions where multiple languages are spoken, inserts must be folded in a way that ensures each language remains clearly separated and easily accessible.
- Frequent Updates: As medications undergo further clinical trials, pharmaceutical companies must update inserts with new data while ensuring the information remains structured and readable post-folding.
- Serialization and Tracking: Some regulatory bodies require pharmaceutical packaging to include unique serial numbers or barcodes for tracking. If these elements are improperly placed or obscured by folding errors, compliance violations may occur.
To overcome these issues, pharmaceutical manufacturers use AI-driven compliance monitoring tools that cross-check inserts against legal guidelines before mass production.
3. High-Speed Production Demands
Pharmaceutical companies manufacture millions of units per month, requiring highly efficient production lines capable of folding thousands of leaflets per hour without sacrificing quality. Some challenges related to high-speed production include:
- Machine Calibration: High-speed folding machines must be precisely calibrated to handle delicate paper materials and prevent misalignment.
- Paper Jams and Misfeeds: Automated folding machines can experience mechanical failures, causing delays and production waste.
- Ink Drying Time: High-speed printing and folding processes must allow sufficient time for ink to dry before folding, or else smudging can occur.
To maintain efficiency, pharmaceutical companies invest in state-of-the-art folding machines with built-in quality control sensors that detect misalignments and prevent errors before inserts enter the packaging stage.
4. Material Selection
The choice of materials used for pharmaceutical inserts plays a crucial role in ensuring durability, clarity, and compliance. Unlike standard commercial printing, pharmaceutical inserts must use specific paper types to withstand multiple folds while remaining readable. Key material considerations include:
- Paper Weight and Thickness: Using paper that is too thick can make folded inserts bulky, while paper that is too thin can tear easily. Most pharmaceutical inserts use lightweight, durable paper ranging from 40 to 60 gsm (grams per square meter).
- Ink Absorption and Coating: Paper must be able to absorb ink properly without causing smudging or fading, especially in folded areas.
- Sustainability Concerns: With growing environmental regulations, many pharmaceutical companies are shifting towards recycled and biodegradable paper options to minimize waste.
By selecting high-quality materials and conducting durability tests, manufacturers can reduce production errors and improve patient experience.
5. Error Prevention
Errors in pharmaceutical folding can have severe consequences, ranging from misinforming patients to legal penalties for non-compliance. Some common errors include:
- Incorrect Folding Patterns: A misaligned fold can cause critical information to be hidden or mixed up, leading to confusion for patients and healthcare providers.
- Overlapping Text or Barcodes: When text or QR codes are folded incorrectly, they can become unreadable, preventing proper tracking and compliance.
- Missing Sections: If an insert is folded incorrectly, some sections may be completely missing or inaccessible.
To combat these risks, pharmaceutical companies implement multi-stage quality control protocols, including:
- Barcode Verification: Ensuring that every leaflet contains scannable barcodes for inventory and compliance tracking.
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR): Using AI-powered scanning technology to detect misprints, missing text, or misaligned folds before inserts reach packaging.
- Automated Folding Inspections: Modern pharmaceutical folding machines are equipped with precision sensors that immediately detect folding errors and prevent defective inserts from continuing in the production process.
The Role of Technology in Pharmaceutical Folding
1. Automated Folding Machines
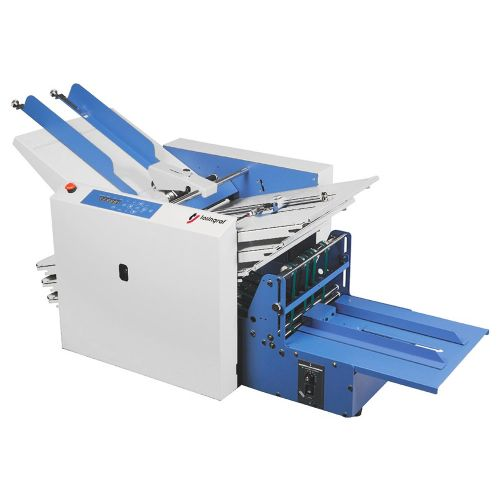

Modern pharmaceutical folding machines use advanced automation to handle high-volume production with extreme precision. These machines can fold thousands of inserts per hour while maintaining exact measurements and creases.
2. Optical Inspection Systems
To prevent misfolded or incorrectly printed inserts from reaching the market, manufacturers use optical inspection systems to detect errors in text alignment, ink smudging, or faulty creasing.
3. Robotic Packaging Integration
Many pharmaceutical manufacturers integrate folding machines with robotic packaging systems, ensuring seamless transition from printing to packaging without human intervention.
4. Digital Printing Innovations
With the rise of digital printing, pharmaceutical inserts can now be printed on-demand, reducing waste and improving production flexibility. High-resolution printing ensures that even the smallest fonts remain clear and legible.
Best Practices for Pharmaceutical Folding
1. Use High-Quality Paper
Selecting the right paper type can significantly impact the durability and readability of pharmaceutical inserts. Lightweight yet sturdy paper is ideal for high-density information inserts.
2. Maintain Strict Quality Control
Implementing multiple checkpoints during the folding process helps eliminate errors. Barcode scanning and AI-based inspections improve accuracy and prevent misprints.
3. Optimize Font and Layout
Pharmaceutical inserts must strike a balance between fitting large amounts of information into a small space while maintaining readability. Proper font selection, spacing, and text alignment ensure clarity.
4. Ensure Compliance with Global Regulations
Different countries have specific requirements for pharmaceutical inserts. Understanding and complying with regulations from the FDA (U.S.), EMA (Europe), TGA (Australia), and other authorities ensures that inserts are legally approved.
5. Leverage Automation for Efficiency
Automated pharmaceutical folding machines reduce production time while improving accuracy. Investing in high-speed, precision folding equipment allows manufacturers to meet high production demands without compromising quality.
The Future of Pharmaceutical Folding
As technology continues to advance, pharmaceutical folding processes are expected to become even more efficient and precise. Emerging trends include:
- Smart Packaging: QR codes and augmented reality (AR) integration in pharmaceutical inserts for interactive patient education.
- Sustainable Materials: The push for eco-friendly and biodegradable paper options to reduce the environmental impact of pharmaceutical packaging.
- AI-Based Quality Control: Machine learning algorithms for real-time error detection in folded inserts.
- On-Demand Printing: Flexible printing solutions that allow small-batch pharmaceutical companies to print inserts as needed, reducing waste.
Pharmaceutical folding is a crucial process in the healthcare and pharmaceutical industry, ensuring that essential medical information is compact, accessible, and easy to read. From precision engineering in automated folding machines to regulatory compliance and innovative printing techniques, every aspect of pharmaceutical folding is designed to enhance patient safety and streamline manufacturing efficiency.
As the industry continues to evolve, companies specializing in pharmaceutical folding must adopt new technologies and best practices to stay ahead of the curve. By prioritizing quality control, automation, compliance, and sustainability, pharmaceutical folding will remain an indispensable component of modern medicine packaging.
At Miniature Folding, we specialize in high-precision pharmaceutical folding solutions, ensuring that every insert meets the highest standards of accuracy, readability, and compliance. Our advanced folding technologies, rigorous quality control processes, and commitment to innovation make us a trusted partner for pharmaceutical companies looking for reliable and efficient folding solutions. Whether you need complex folded inserts or high-volume production capabilities, Miniature Folding delivers unmatched expertise in pharmaceutical folding to help you meet industry demands with confidence.
Related Insights
Keep Exploring Sustainable Packaging Trends
 Read more
Read moreWhat Makes a Folding Insert High Quality? Key Features to Look For
High Quality Folding Inserts In the competitive landscape of packaging, folding inserts or folding sheets
 Read more
Read moreThe Ultimate Showdown: How Barcode Scanning Tags Stack Up Against QR Codes for Product Tracking
In the rapidly evolving landscape of inventory management and product tracking, businesses are increasingly relying
 Read more
Read moreEnhancing Patient Safety: How Folded Inserts Outperform Digital Information Leaflets
In the healthcare sector, effective communication is crucial, especially when it comes to patient safety.